Studing the evolution of the human brain is an exciting endeavour to unravel what distinguishes human from its close relatives, ancient hominins and primates. A combination of computational neuroanatomy and evolutionary genetics has a great potential of answering questions about the evolution of cognitive traits, including extinct species, which are otherwise impossible to investigate.
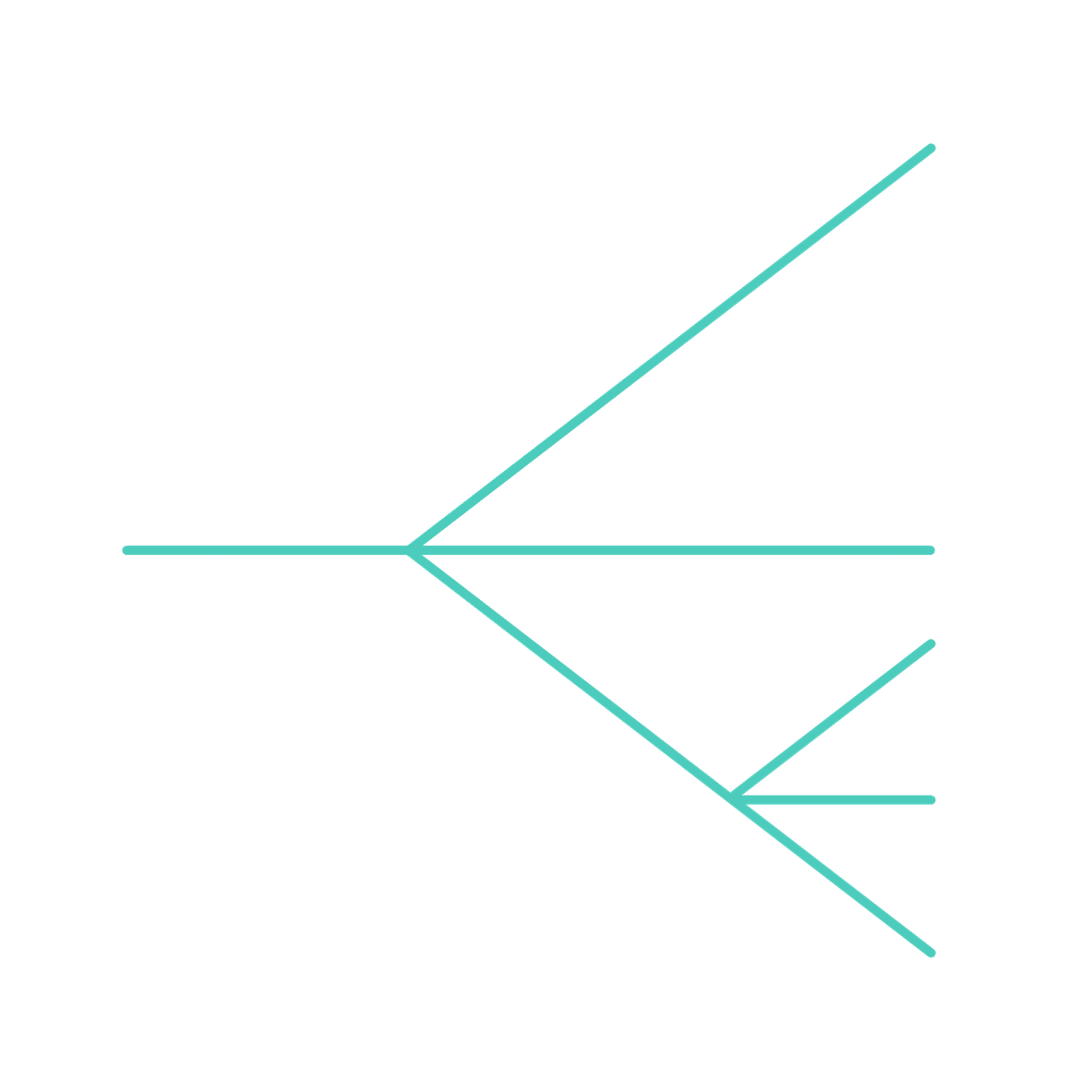
The evolution of closely related species is often accompanied by Incomplete Lineage Sorting (ILS), which leads to differences in evolutionary species tree and separate gene trees. The figure is the visualisation of different expected scenarious of gene evolution among Gorilla, Chimp, Human, and its ancient relatives, Denisovan and Neanderthal. To study the evolution of cognitive traits we performed evolutionary analysis by accounting for ILS and providing more robust results for the downstream analysis.
In this project I studied evolution of brain-expressed genes by tracing changes of non-synonymous to synonymous evolutionary rates (dN/dS) along branches of primate evolutionary gene-trees. I collected data for modern species and prepared corresponding protein coding sequences for ancient hominins and performed complete evolutionary analysis, from alignments to gene-trees, and subsequent computation of dN/dS ratios. The results of evolutionary analysis were further used as an input for computational neuroanatomy analysis.
Contributions:
- Data collection: collected protein coding sequences for one-to-one orthologs (brain-expressed genes) for modern species
- Data preparation: prepared corresponding protein coding sequences for ancient hominins (Denisovan and Neanderthal) by extracting SNPs from published VCF files, mapping them to the human reference, cuting out protein coding sequences by using exon positions extracted from ensembl database
- Preparation of per-gene multiple sequence alignments
- Evolutionary model testing
- Inference of phylogenetic gene-trees (multiple independent runs per gene)
- Performed tree topology tests
- Designed an approach to account for Incomplete Lineage Sorting for more robust downstream analysis
- Performed dN/dS analysis
- Results parsing and formating for downstream analysis
- Wrote parts of the manuscript, results visualisation